Embark on a virtual journey through the diverse landscapes and rich history of Victoria, Australia. From bustling cities to serene beaches, from historic landmarks to modern infrastructure, our comprehensive map of Victoria unveils the treasures of this captivating state.
Uncover the natural beauty of Victoria’s diverse regions, delve into its fascinating past, navigate its transportation network, discover its tourism hotspots, and explore its thriving industries. Let our map guide you through the heart of Victoria, revealing its unique character and boundless opportunities.
Geographical Features
Victoria is Australia’s smallest mainland state, but it packs a punch when it comes to geographical diversity. From the snow-capped peaks of the Victorian Alps to the rugged coastline of the Great Ocean Road, Victoria has something to offer everyone.
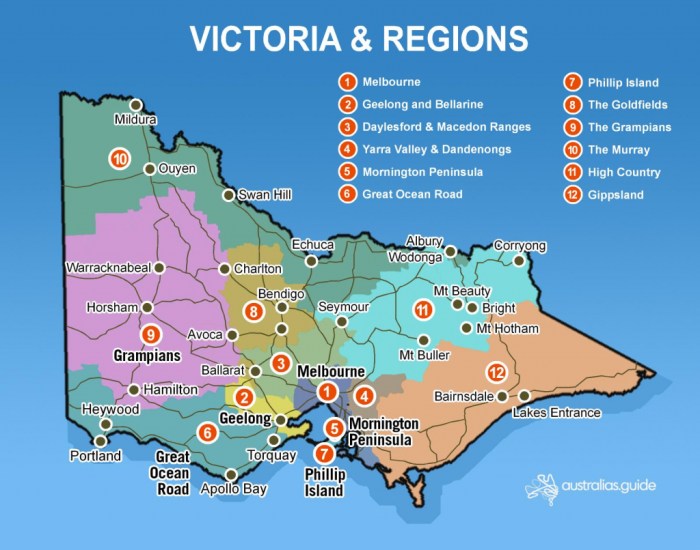
The state is divided into nine major geographical regions, each with its own unique character and attractions.
Major Geographical Regions of Victoria
The major geographical regions of Victoria are:
- The Grampiansare a rugged mountain range in western Victoria, known for their stunning sandstone cliffs and waterfalls.
- The Great Dividing Rangeruns through the center of Victoria, forming the state’s highest peaks, including Mount Bogong, the highest point in Victoria.
- The Goulburn Valleyis a fertile agricultural region in northern Victoria, known for its vineyards and orchards.
- The Wimmerais a dry, inland region in western Victoria, known for its sheep and wheat farming.
- The Malleeis a semi-arid region in northern Victoria, known for its mallee eucalypts and salt lakes.
- The Gippslandis a large, diverse region in eastern Victoria, known for its forests, lakes, and coastline.
- The Central Highlandsare a mountainous region in central Victoria, known for their forests, waterfalls, and gold mining history.
- The West Coastis a rugged, sparsely populated region in western Victoria, known for its shipwrecks and coastal scenery.
- The Port Phillipregion is a densely populated region in southern Victoria, home to Melbourne, the state capital.
Read more: Lindfield New South Wales: A Thriving Suburb with Rich History and Modern Charm
Historical Sites and Heritage

Victoria is home to a rich tapestry of historical sites and heritage landmarks that tell the story of its fascinating past. From the Eureka Stockade, where miners fought for their rights, to Sovereign Hill, a living museum that brings the gold rush era to life, Victoria’s historical sites offer a glimpse into the events that shaped the region.
The Royal Exhibition Building, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, stands as a testament to Victoria’s architectural prowess and its role in hosting the first World’s Fair outside of Europe. These historical sites not only serve as reminders of the past but also provide valuable insights into Victoria’s cultural and social development.
Historical Timeline
- 1835: John Batman establishes a settlement at Port Phillip.
- 1851: Gold is discovered at Ballarat, triggering a gold rush.
- 1854: The Eureka Stockade rebellion takes place, leading to the establishment of democratic reforms.
- 1880: The Royal Exhibition Building is constructed for the Melbourne International Exhibition.
- 1901: Victoria becomes a state of the newly federated Commonwealth of Australia.
- 1956: The Olympic Games are held in Melbourne.
Read more: Chermside: Brisbanes Vibrant Suburb with Unrivaled Lifestyle and Convenience
Transportation and Infrastructure
Victoria’s transportation network is a vital part of the state’s economy and quality of life. The state has a comprehensive network of highways, railways, and airports that connect it to the rest of Australia and the world. However, Victoria’s transportation infrastructure is facing a number of challenges, including congestion, aging infrastructure, and the need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Challenges and Opportunities
One of the biggest challenges facing Victoria’s transportation infrastructure is congestion. The state’s population is growing rapidly, and this is putting a strain on the transportation network. Congestion can lead to delays, increased travel times, and air pollution.Another challenge facing Victoria’s transportation infrastructure is aging infrastructure.
Many of the state’s roads, bridges, and railways were built decades ago and are in need of repair or replacement. This can lead to safety hazards and disruptions to service.Finally, Victoria’s transportation infrastructure needs to be more sustainable. The transportation sector is a major source of greenhouse gas emissions, and the state needs to find ways to reduce its emissions.
This can be done by investing in public transportation, walking, and biking, and by making vehicles more fuel-efficient.Victoria’s transportation infrastructure is facing a number of challenges, but there are also a number of opportunities. The state can invest in new technologies to improve the efficiency of its transportation network.
It can also work with other states and the federal government to develop a more sustainable transportation system. By taking these steps, Victoria can ensure that its transportation infrastructure meets the needs of its growing population and economy for years to come.
Read more: Discover Tasmanias Capital: A Guide to Hobarts Map and Must-Visit Attractions
Tourism and Attractions: Map Of Victoria
Victoria boasts an abundance of tourist attractions that cater to diverse interests. From pristine beaches to sprawling national parks, world-class wineries to historic landmarks, Victoria offers a plethora of experiences that entice visitors year-round.
Emerging tourism trends in Victoria point towards an increasing demand for sustainable and experiential travel. Visitors seek authentic and immersive experiences that connect them with the region’s natural beauty, cultural heritage, and local communities.
Beaches
Victoria’s coastline stretches for over 2,000 kilometers, offering a diverse range of beaches to suit every taste. From the iconic surf breaks of Bells Beach to the tranquil waters of Port Phillip Bay, Victoria’s beaches provide ample opportunities for swimming, surfing, fishing, and sunbathing.
- Bells Beach: Known for its world-renowned surf breaks and annual Rip Curl Pro surfing competition.
- Torquay: A popular beach town that offers a range of water sports and activities, including surfing, paddleboarding, and kayaking.
- St Kilda Beach: A vibrant and cosmopolitan beach in Melbourne, known for its colorful bathing boxes and lively atmosphere.
National Parks, Map of victoria
Victoria is home to a vast network of national parks that protect a diverse range of landscapes, from towering mountain ranges to pristine rainforests. These parks offer opportunities for hiking, camping, wildlife viewing, and nature appreciation.
- Grampians National Park: A rugged and picturesque park known for its towering sandstone cliffs, waterfalls, and wildflowers.
- Wilsons Promontory National Park: A peninsula at the southernmost tip of mainland Australia, renowned for its pristine beaches, coastal walks, and abundant wildlife.
- Great Otway National Park: A coastal park that features towering waterfalls, ancient rainforests, and dramatic coastline views.
Wineries
Victoria is a renowned wine region, producing a wide range of award-winning wines. The Yarra Valley, Mornington Peninsula, and Geelong regions are particularly well-known for their Chardonnay, Pinot Noir, and Shiraz.
- Yarra Valley: Home to some of Victoria’s most prestigious wineries, known for its cool-climate wines and picturesque vineyards.
- Mornington Peninsula: A coastal wine region known for its Pinot Noir and Chardonnay, as well as its stunning ocean views.
- Geelong: A historic wine region that produces a range of wines, including Chardonnay, Sauvignon Blanc, and Cabernet Sauvignon.
Cultural Landmarks
Victoria is rich in cultural history, with numerous museums, galleries, and historical sites that showcase the region’s heritage.
- Melbourne Museum: A world-renowned museum that houses a vast collection of natural history, cultural artifacts, and scientific exhibits.
- National Gallery of Victoria: One of Australia’s leading art museums, with a collection that spans from ancient to contemporary art.
- Eureka Stockade: A historical site in Ballarat that commemorates the Eureka Rebellion, a significant event in Australian history.
Read more: Postcode Toowoomba QLD: A Comprehensive Guide to the Citys Postal Districts
Economic and Industry
Victoria’s economy is diverse and robust, with key industries including manufacturing, agriculture, and tourism. These industries contribute significantly to the state’s economic growth and employment.
Manufacturing
Victoria is a major manufacturing hub in Australia, with a strong presence in automotive, aerospace, and food processing. The state’s manufacturing sector is known for its innovation and technological advancements, and is a key driver of economic growth.
Agriculture
Victoria is one of Australia’s leading agricultural states, with a strong focus on livestock, dairy, and horticulture. The state’s agricultural sector is highly productive and contributes significantly to the national food supply.
Tourism
Victoria’s tourism industry is thriving, with the state attracting both domestic and international visitors. The state’s diverse attractions, including natural wonders, cultural landmarks, and world-class sporting events, make it a popular destination for tourists.
Potential for Diversification
While Victoria’s economy is strong, there are opportunities for diversification to further enhance its economic growth. Potential areas for diversification include renewable energy, biotechnology, and financial services. By investing in these sectors, Victoria can position itself for continued economic success in the future.
Read more: Postcode Chermside: An Oasis of Suburbia and Convenience
Final Review
Our exploration of Victoria concludes with a deeper appreciation for its geographic diversity, historical significance, transportation infrastructure, tourism attractions, and economic strengths. Whether you’re a local resident, a prospective visitor, or simply curious about this vibrant Australian state, this map has provided a comprehensive overview of Victoria’s many facets.